Back to the Data Model
Model-View-Presenter from Microsoft is related to MVC.
Here are the Specifications
I have derived these Specifications from the Wikipedia entry for MVC.
As a design pattern MVC encompasses more of the architecture of an application than is
typical for a design pattern.
Pattern description
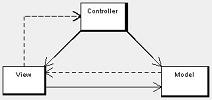
Model–view–controller is both an architectural pattern and a design pattern, depending on where it is used.
As an Architectural Pattern
It is common to split an application into separate layers that run on different computers:
the presentation/user interface (UI)
business logic,
data access.
In MVC the presentation layer is further separated into view and controller, resulting in three layers.
MVC is often seen in web applications, where the view is the actual HTML or XHTML page, and the controller
is the code that gathers dynamic data and generates the content within the HTML or XHTML.
Finally, the model is represented by the actual content, which is often stored in a database or in XML nodes,
and the business rules that transform that content based on user actions.
Though MVC comes in different flavors, control flow is generally as follows:
The user interacts with the user interface in some way (for example, presses a mouse button).
The controller handles the input event from the user interface, often via a registered handler or callback.
The controller notifies the model of the user action, possibly resulting in a change in the model's state.
For example, the controller updates the user's shopping cart).[4]
A View uses the Model indirectly to generate an appropriate user interface
(for example, the view lists the shopping cart's contents).
The view gets its own data from the model.
The model and controller have no direct knowledge of the view.
The user interface waits for further user interactions, which restarts the cycle.
Some implementations such as the W3C XForms also use the concept of a dependency graph to
automate the updating of views when data in the model changes.
By decoupling models and views, MVC helps to reduce the complexity in architectural design and to
increase flexibility and reuse of code.
As a design pattern
MVC encompasses more of the architecture of an application than is typical for a design pattern.
Model
The Model is the domain-specific representation of the information on which the application operates.
Domain logic adds meaning to raw data (for example, calculating whether today is the user's
birthday, or the totals, taxes, and shipping charges for shopping cart items).
Many applications use a persistent storage mechanism (such as a database) to store data.
MVC does not specifically mention the data access layer because it is understood to be
underneath or encapsulated by the model.
View
The View renders the model into a form suitable for interaction, typically a user interface element.
Multiple views can exist for a single model for different purposes.
Controller
The Controller processes and responds to events (typically user actions) and may indirectly
invoke changes on the model.
[edit] Selected frameworks
Barry's Comments :-
From these Specifications, we can identify a need for :-
Controller
Event
Model
Users
View
Barry Williams
6th. February 2009
Principal Consultant
Database Answers