
Welcome to our Tutorial on Data Modelling.
|
1) GETTING STARTED :


In this Tutorial, we follow two young visitors to Windsor Castle in England.
Our visitors are Dimple, a 10-year old girl, who likes sightseeing and icecream and
Toby, Dimple's 12-year-old brother, who likes sightseeing and databases.
|
2) WHAT SHALL WE DO TODAY ? :
[Dimple] : Toby, It's great being in London which is so exciting and buzzing.
[Toby] : I'm glad you like it, Dimple. What would you like to do today ?
[Dimple] : I'd like to visit Windsor Castle, because it's one of the most popular tourist attractions in England, and it's easy to get to from London.
[Toby] : OK. Let's go ...
|
3) WINDSOR CASTLE

Windsor Castle is very beautiful and was built in the year 1068.
|
4) WINDSOR SHOPS

[Dimple] Wow, Toby, there are so many Banks, Cafes, Pubs, Restaurants, Shops, Wine Bars and Hospitals !!!
[Toby] : Yes, let's start thinking about our Data Model.
The other thing that we see when we look around is people - lots of people.
|
5) STARTING OUR DATA MODEL :

[Dimple] : How do we get started ?
[Toby] : Well, we know that we have People and Places.
The simplest start is to call all these places Establishments.
Then we simply have different kinds of Establishments.
And we have people - local people, visitors, people working here, people here on business and so on.
[Dimple] : Hmmm - so how do we translate what we know to help us get started with our Data Model !!!
|
6) IDENTIFIERS AND PRIMARY KEYS :
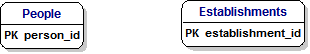
[Dimple] : Toby, I am one of these People so how I am I going to identify myself from everybody else.
[Toby] : We will give everybody a Unique Identifier and every Establishment its own unique Identifier.
When we use these we call them Primary Keys, and show them in the diagram with a PK on the left-hand side.
[Dimple] : That sounds good, Toby, but I don't know what it means.
[Toby] : Well, Dimple, let's look at how we use these Identifiers ...
|
7) RELATIONSHIPS AND FOREIGN KEYS :

[Toby] : Dimple, now we can add some interesting details because we know that one person can visit many Establishments.
We also know that one Establishment is visited by many Visitors.
Then we call this a Many-to-Many Relationship between People and Establishments.
|
8) RELATIONSHIPS AND FOREIGN KEYS :
To make it easier for you to understand I have expanded the Many-to-Many Relationship into two different things, which are called One-to-Many Relationships.
[Dimple] : So Toby, is that like saying that One Person can make Many Visits to many Establishments ?
[Toby] : Yes, Dimple - that's great - and we can also say that One Establishments can have Visits from many People.
|
9) RELATIONSHIPS AND FOREIGN KEYS :
At this point, we can show how all these boxes are related, and that is a very big step, because it takes us to the idea of 'Relationships'.
And now we can see how useful our Identifiers can be because we can include the Person and Establishment Identifiers in our Visits table. Then the Person_ID field becomes a link to a record for a Person in the Person Table.
This link is what is called a Foreign Key and we can see it's shown with 'FK' on the left-hand side.
|
10) PRODUCTS AND PRODUCT TYPES :
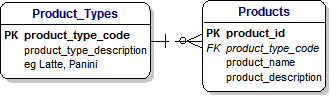
[Dimple] : Toby, when we go into a shop we want to buy something.
And there are thousands and thousands of possibilities.
How do we deal with all that in our little Data Model ?
[Toby] : Well Dimple, it's really quite easy. It's like all our Modelling where we look for simple patterns that cover many situations.
[Dimple] : Hmm - I don't know what that means. Maybe if you showed me I might understand it.
[Toby] : OK.
|
11) PRODUCTS AND PRODUCT TYPES :
Everything that we buy is called a Product, and all we have to do is simply define the type of each Product - such as a Coffee, Muffin or a Newspaper.
Then we draw a little box called Products and say that every Product has a Type.
In other words, there is a Relationship between the Products and Product_Types boxes.
The lines are called Relationships and they are very important in Data Modelling.
We are now creating an Entity-Relationship Diagram or "ERD".
|
12) PRODUCTS, TYPES AND PRODUCT HIERARCHIES:

[Dimple] : Toby, when we look closely at the Menu Board to try to decide what to order we can see lots of possibilities
But after a while we can see a pattern that helps us decide.
How do we deal with all that in our little Data Model ?
|
13) PRODUCTS, TYPES AND PRODUCT HIERARCHIES:
[Toby] : Well Dimple, it's really quite easy.
We define something called a Hierarchy.
Hierarchies are very common and simply mean any situation where there are Parents, Children, Gand-children and so on.
|
14) PRODUCTS, TYPES AND PRODUCT HIERARCHIES:
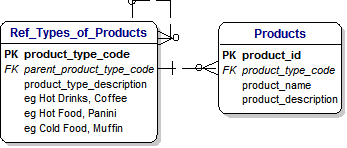
On the Starbucks Menu we can see a simple example of 'Expresso' and under it a number of different drinks.
My favourite is Caramel Macchiatto.
So in this case, the top-level of our hierarchy is a Product Category called Expresso, and the next level down is a Product called Caramel Macchiatto.
|
15) PRODUCTS, TYPES AND PRODUCT HIERARCHIES:
[Dimple] : OK. That sounds OK.
[Toby] : Finally, we show this Herarchy by a dotted line that in the top-right hand corner in the Entity called 'Ref_Types_of_Products'.
This is formally called a 'Reflexive' relationship and informally 'Rabbits-Ears'
|
16) TYPES OF PEOPLE :
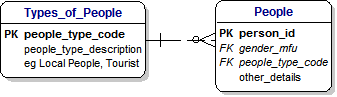
[Dimple] : Toby, that looks OK.
I guess we can deal with Types of People the same way, can we ?
[Toby] : Yes, Dimple, and Types of Establishments as well.
[Dimple] : OK, that sounds sensible. And do they use these Identifiers in a Database ?
[Toby] : Yes, and what is even better is that the Database will automatically generate a new unique Identifier for you and your Visits and Purchases in case you want to get a refund later.
|
17) TYPES OF ESTABLISHMENTS:
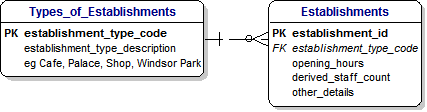
[Dimple] : Toby, that looks OK.
I guess we can deal with Types of Establishments the same way, can we ?
[Toby] : Yes, Dimple.
[Dimple] : OK, that sounds sensible. And do they use these Identifiers in a Database ?
[Toby] : Yes, and what is even better is that the Database will automatically generate a new unique Identifier for you and your Visits and Purchases in case we want to keep track of things, like maybe you want to get a refund later
so we need to get your details from the Database.
|
18) TYPES OF ESTABLISHMENTS:
[Toby] : Finally, let's a little more talk about Establishments.
One special thing about Windsor is that it has a Castle where the Queen lives and a very large Royal Park, where she keeps Deer.
But when we think about these things, we find that we can simply fit into our definition of Establishments, because they take Visitors, and have opening hours.
|
19) VISITS TO THE SHOPS :

[Dimple] : Toby, with so many People, Establishments and Purchases how do they keep track of everything ?
[Toby] : Well, Dimple, by this time, everything has its own Identifier that is used wherever they need to keep track.
[Dimple] : OK, that sounds sensible. And do they use these Identifiers in a Database ?
[Toby] : Yes, and what is even better is that the Database will automatically generate a new unique Identifier for you and your Visits and Purchases in case you want to get a refund later.
|
20) VISITS AND PURCHASES :

[Dimple] : Toby, with so many People, Establishments and Purchases how will we keep track of everything ?
[Toby] : Well, Dimple, by this time, everything has its own Identifier that is used wherever they need to keep track.
[Dimple] : OK, that sounds sensible. And do they use these Identifiers in a Database ?
[Toby] : Yes, and what is even better is that the Database will automatically generate a new unique Identifier for you and your Visits and Purchases in case you want to get a refund later.
|
21) PEOPLE AND STAFF:
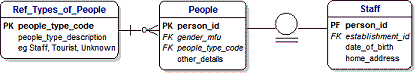
[Toby] : Dimple, let's take a closer look at the different types of people we can find in Windsor.
[Dimple] : OK, Toby. I hope I don't have to think too much because I might get a headache ?
[Toby] : No, Dimple, I will do the thinking and talking and all you have to do is nod your head when you understand.
[Dimple] : OK, Toby. I promise to do that.
|
22) PEOPLE AND STAFF:
[Toby] : We already said that we have Local People and Tourists.
Some of these Local People are shoppers and some of them will be working in the shops.
We will call the workers 'Staff' and we know more about them than we do about the Visitors.
For example, we will probably know the Gender of everybody just by looking at them.
|
23) PEOPLE AND STAFF:
For Staff, we will usually also know their Data of Birth and their Home Address.
Therefore, although they are all People, we know more about Staff than we do about Visitors.
In Data Modelling we have a very powerful approach that we call Inheritance that we can use here.
It's shown by the funny circle with two lines.
If we want to describe this in English, we would say that Staff inherit the People_Type_Code and Gender from the parent Entity of People, and in addition, they have a Date of Birth and Home Address.
|
24) PEOPLE AND STAFF:
Does that make sense, Dimple ?
[Dimple] : I think so, Toby.
Is it like saying that we inherit having two arms and two legs from our Parents because they have two arms and two legs, but that we have also have things that are just us ?
[Toby] : Yes, Dimple - that's great - let's take a break and do some shopping !!!
[Dimple] : I like the sound of that, Toby. Can I have an icecream now?
|
25) STAFF, ESTABLISHMENTS AND ONE-TO-MANY RELATIONSHIPS :
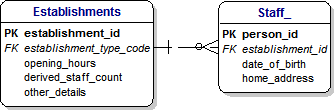
[Dimple] : Toby, how do we specify that Staff work in Establishments ?
[Toby] : Dimple, that's a very good question.
Fortunately, the answer is very easy, and we simply add a One-to-Many Relationship between the Staff and the Establishment.
|
26) ONE-TO-MANY RELATIONSHIPS AND FOREIGN KEYS :
[Toby] : In English, we would say that a One-to-Many Relationship means every member of Staff must work in one Establishemnt and every Establishment can employ many members of Staff.
In the diagram, we show this with a Foreign Key by the establishment_id field in the Staff Entity.
So if we look closely at the Staff Entity, we will see 'FK' by the establishment_id field.
[Dimple] : OK, I can see how the Identifiers are very important.
[Toby] : I am glad to hear it, Dimple.
|
27) RULES FOR DATA MODELLING :
There is one more thing I have to say.
We are learning Data Modelling and one important thing about Data Modelling is that it has to follow a set of Rules.
These Rules help us to produce good Data Models and so they they are very important.
|
28) THE 'NO DERIVED FIELDS' RULE :
One of the Rules is that we cannot include any bits of data that can be derived from any other bits of data.
For example, we usually want to know how many people work in a Shop or Cafe.
Therefore we include a Staff Count field with the Establishment.
|
29) FINDING DERIVED FIELDS :
When it comes to finding the derived value that goes in here, we will count the records in the Staff Table for each Establishment.
Therefore, it's a derived Field and we call it a name that starts with 'derived_' to make things clear.
Does that sound sensible, Dimple ?
[Dimple] : I suppose so, Toby.
But I've got a headache, can we go for an icecream now ?
|
30) REFERENCE DATA :
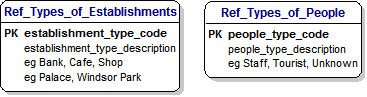
[Toby] : Dimple, we have talked about Reference Data for Types of Establishments and People.
I have given them both names that begin with 'Ref_' to make it clear that they are Reference Data.
This means that the values don't change much and I can use them to define what the valid values can be.
|
31) BRINGING IT ALL TOGETHER :
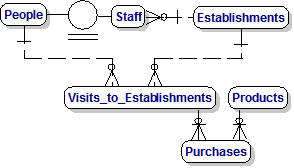
[Toby] : Dimple, if we bring together everything we have talked about, we will have a good Data Model that any professional would be proud of.
[Dimple] : OK, Toby. Do you think I will understand it ?
|
32) BUSINESS RULES :
[Toby] : Let me help you understand it by making a list of the Business Rules for our Model :-
People can be either Staff or Visitors.
Products can be Caramel Machiatto , Panini and so on.
Staff have a Date of Birth and a Home Address.
People can make Visits to Establishments.
During a Visit they can purchase Products.
[Toby] : OK, Dimple - we have a very nice Data Model and now we can take a break.
[Dimple] : That's great, Toby - can I have an icecream ?
|
33) PF KEYS :
Sure, but before we do I should say something about PF, which appears in the Staff Table.
It's unusual and it's called PF because it means a field which is a Primary Key in the Staff Table and a Foreign Key to the People Table.
[Dimple] : Hmmm, I've got a headache, Toby - can we please go an get an icecream ?
[Toby] : OK, Dimple. You've been a very good girl and you deserve a break.
|
34) ICECREAM :

[Toby] : Dimple, I 've got some wonderful news for you.
[Dimple] : I'm glad to hear it, Toby - what is it ?
[Toby] : Your favourite Baskin-Robbins icecream is here in Windsor ;)
[Dimple] : Toby, are you teasing me ?
[Toby] : No, Dimple - look, there it is across the road from Windsor Castle !!
[Dimple] : Wow - I can have my favourite Butter Pecan icecream.
|
35) TOPICS WE HAVE COVERED :
- Hierarchies,Identifiers and Inheritance
- One-to-Many and Many-to-Many Relationships
- Primary Keys, Foreign Keys, PF Keys and Reference Data
|
36) PLEASE EMAIL ME
 I hope you have found this Tutorial fun and useful.
I hope you have found this Tutorial fun and useful.
Please email me with your questions or suggestions.
Barry Williams
Principal Consultant
Database Answers Ltd.
London, England
© DatabaseAnswers.org 2009
|